Recycle Bin
The Recycle Bin has long been a part of Content Management (Extended ECM). It was originally made part of the core product back in Content Server 10, update 11. (September 2013). Despite it's long history in the product I occasionally get questions on how it works, and how it behaves.
This blog post will run through the fundamentals of this function of the product.
Document Deletion process
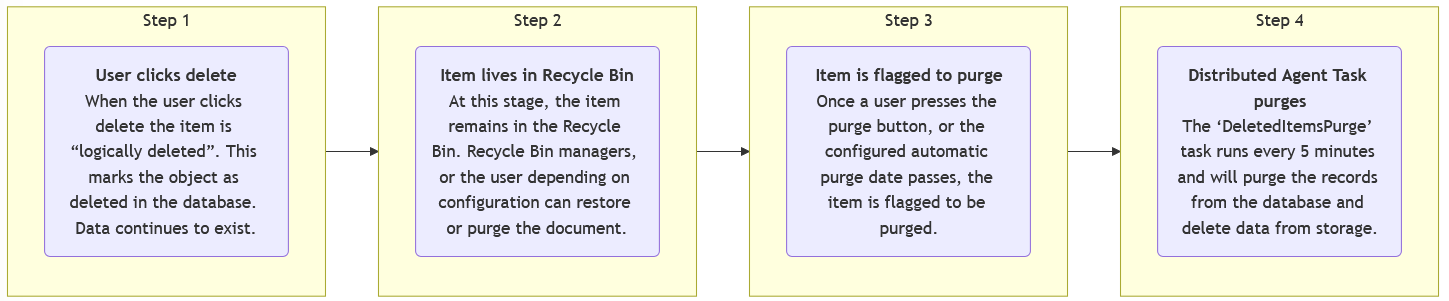
Step 1: User clicks delete
When the user clicks delete, the item is not 'Moved' to a new location in the traditional sense. The ParentID of the object remains the same and instead it is marked as deleted. This allows Content Management to process many deletes very quickly.
- The DTreeCore row has the Deleted column is incremented by 1, this value being larger than 0 on any given row indicates that the item is deleted and will hide it from view.
- The DtreeCore name is updated to the GUID of the object.
- A record is inserted into DDeleteItemsNodes containing information such as the recycle date and who deleted the object.
- Records are created for each enabled multilingual metadata in DDeletedItemsNames_[X] storing the multilingual name.
At this stage the item is logically deleted and residing in the recycle bin.
Step 2: The Item in Recycle Bin
Based on the configuration of the system users may or may not have access to see their deleted items, however Recycle Bin managers will be able to see all content.
- Browsing the recycle bin is a list of items, by default ordered by deletion date with the most recently deleted presented at the top.
- Only items with a deleted value of 1 are shown.
- An item with a deleted value of 2, was deleted. Then its parent container was also deleted. We will then only show the parent folder in the Recycle Bin.
Content inside the Recycle Bin is ‘frozen’ and will not be impacted by things such as Category and Attribute pushes from their parent container.
If a user selects restore, they can return the item to its original location. It’s deleted flag will be reset to zero and the rows cleaned up, and object named back as it was prior.
Step 3: The item is flagged to purge
Every five minutes an agent runs (FiveMinuteAgent) and if there are items to purge based on the configured policy by the Administrator. A task is created to purged those items.
Additionally, users can manually purge objects from the Recycle Bin based on their permissions. This will generate a task to purge the object.
Either of these actions will update the DTreeCore row for the item to have a Deleted value of -1. This signals to the system that the item is in a purging state and will be removed from the system. Once the Distributed Agent task runs it will purge the objects from the system.
Step 4: The item is flagged to purge
When the item is flagged to be purged the Deleted column in DTreeCore is moved to -1.
The DeletedItemsPurge task will:
- Iterate through all the items marked Deleted -1
- Purge them from the system cleaning up rows from the database.
- For containers, the task will iterate to the bottom of the hierarchy and work upwards.
- Insert rows into the Audit trail completing the lifecycle of the document.
Configuration
The Recycle Bin has some limited configuration. The majority of Administrators have likely not changed many of these settings since the product was introduced, however I'll walk through a few concepts.
Restorable vs Non-Restorable objects
Items that are restorable are placed in the Recycle Bin when they are deleted. They can be restored after deletion. Items that are non-restorable are purged immediately and cannot be restored.
Changing these settings is not retroactive, anything already within the recycle bin will remain there if you change that specific subtype to be non-restorable.
Auto Purge and View Options
Besides the restorable types, you can configure automatic purge and define the date. This is the time that is leveraged by the FiveMinuteAgent in order to generate purge tasks.
You can also define user access to the Recycle Bin, as well as what filters they would have access to.
Many customers do not permit ordinary users to see all deleted content across the system. Instead opting to restrict that to Recycle Bin Administrators.
Back to post listing